Permissions in Embedding
You can control permissions in Zenlytic via access controls using both access filters (row-based) and access grants (column-based). Docs on those are here.
Setting up the access permissions
To start, you'll define the logic to determine when an access grant is allowed or not allowed. For example, with these definitions, which are found in the model file:
version: 1
type: model
name: demo
connection: demo_snowflake
access_grants:
- name: events_access
user_attribute: events
allowed_values:
- has_events
- name: revenue_access
user_attribute: revenue
allowed_values:
- has_revenue
- name: sessions_access
user_attribute: sessions
allowed_values:
- has_sessions
...
In this example, if you pass the user attribute {"revenue": "has_revenue"} the session will have access to all tables governed by the revenue_access access grant. Similarly, if you pass the user attribute with any other value besides "has_revenue" the session will not have access to the tables governed by that access grant (e.g. {"revenue": "no_revenue"}).
You can restrict a view or a field with an access grant by name, by adding the property required_access_grants with an array of the grants the user must possess:
required_access_grants:
- revenue_access
Full Example
Using the above model as our model, consider the following four views:
name: orders
type: view
model_name: demo
default_date: order_created_at
required_access_grants:
- revenue_access
fields:
...
name: events
type: view
model_name: demo
sql_table_name: DEMO_PROD.EVENTS
default_date: event_timestamp
required_access_grants:
- events_access
name: pg_orders
type: view
model_name: pg_demo
sql_table_name: demo.public.orders
default_date: order_created_at
required_access_grants:
- revenue_access
name: sessions
type: view
model_name: demo
sql_table_name: wcb.sessions
default_date: session_date
required_access_grants:
- sessions_access
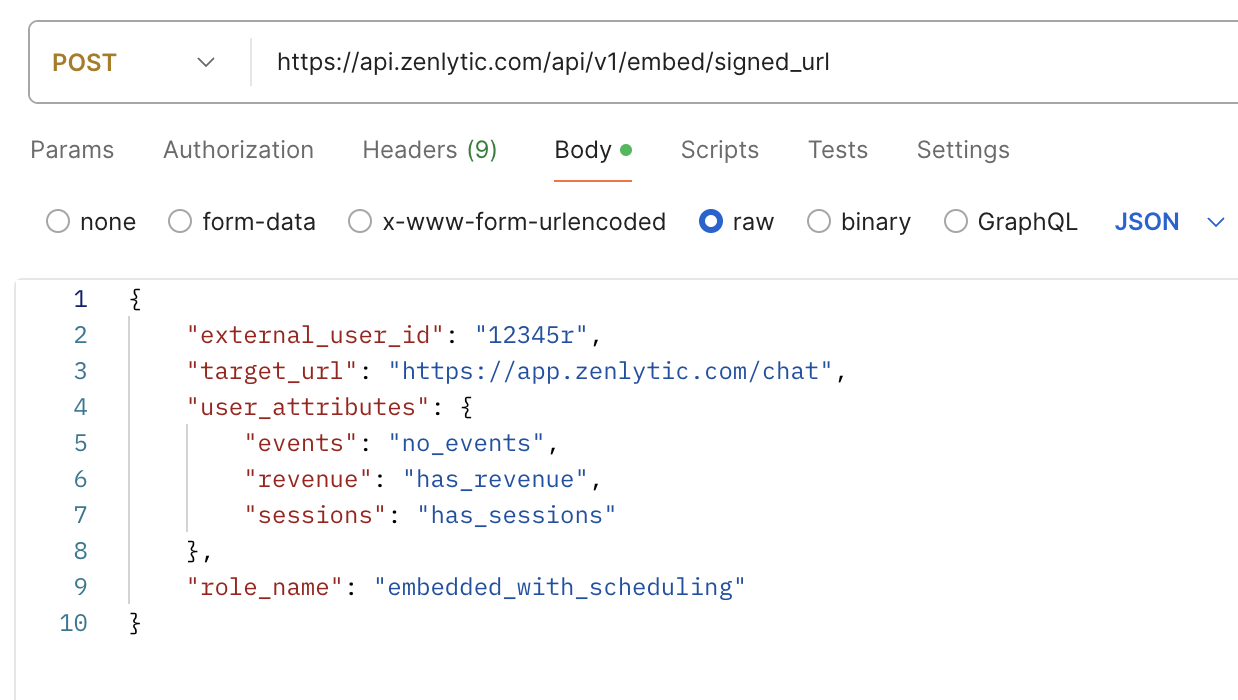
When requesting the signed API for the session if you pass the set of user_attributes
{
"events": "has_events",
"revenue": "no_revenue",
"sessions": "no_sessions"
}
Which looks like this in Postman

The session that is generated will NOT have access to any of pg_orders, orders, or sessions. It will only have access to the events table (assuming these four tables are the only ones in our model). Zoë will not be able to see those three tables the user does not have access to, and will have no idea that they exist.
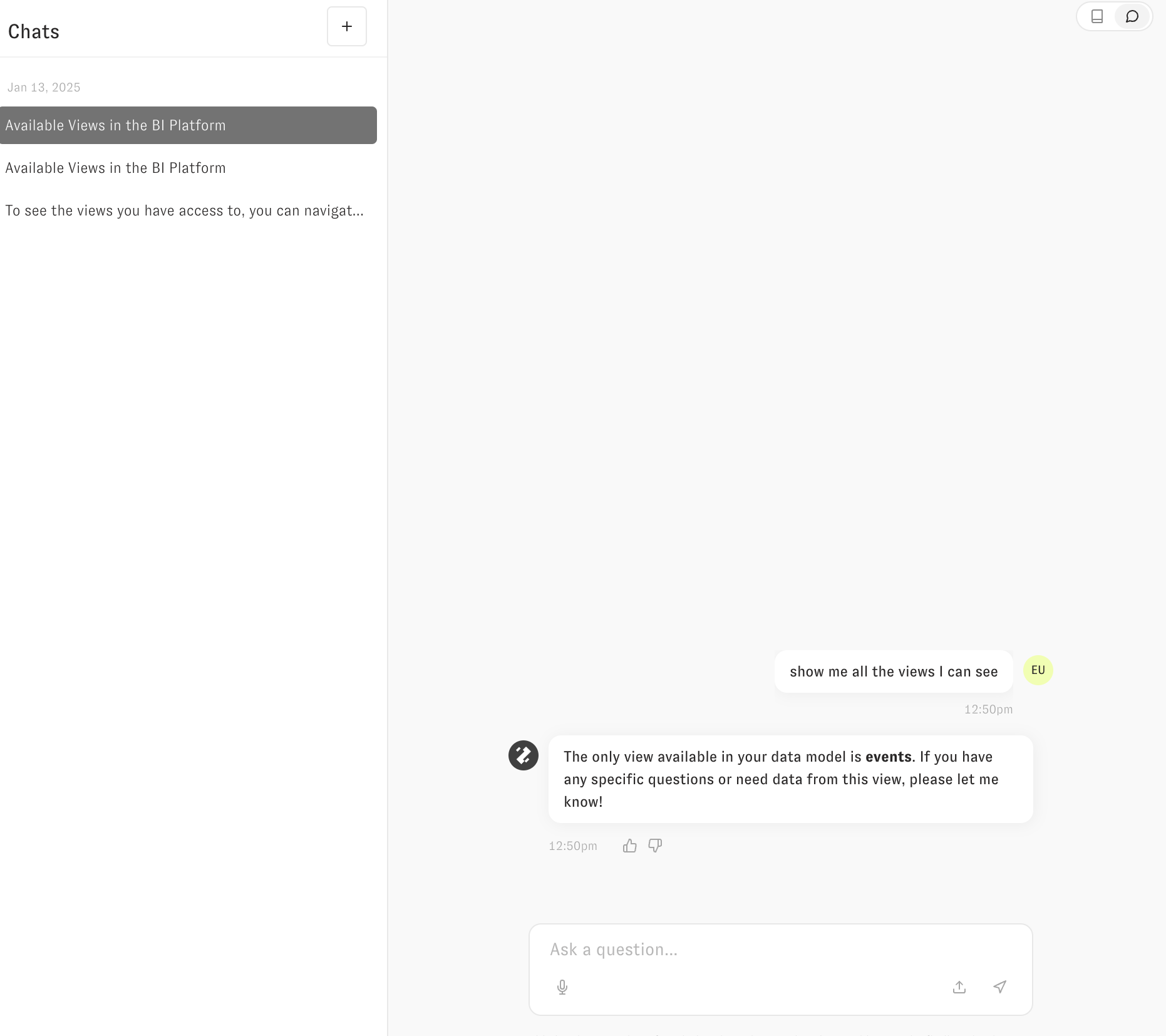
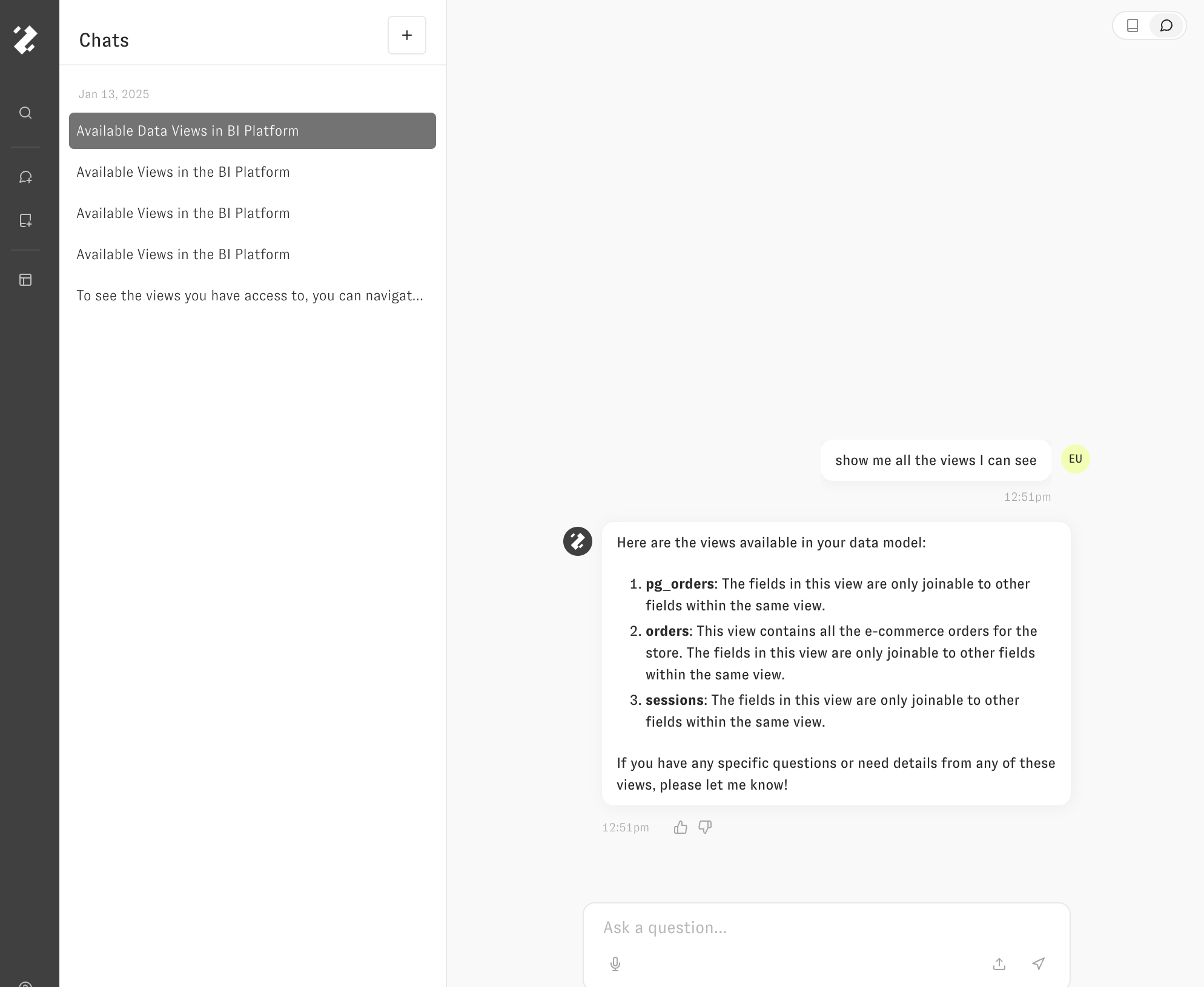
Conversely, if you pass the following user_attributes
{
"events": "no_events",
"revenue": "has_revenue",
"sessions": "has_sessions"
}
The user will have access to the pg_orders, sessions, and orders tables, but will NOT have access to the events table.
You can apply similar logic to fields as well to define more granular permissions inside of tables.